 Field Effect transistors (FETs)
Field Effect transistors (FETs) Field Effect transistors (FETs)
Field Effect transistors (FETs)| Components | Resistors | Capacitors | Inductors | Crystals | Diodes | Transistors |
| FETs | Triacs | Infra-red | ICs | LEDs | Speakers and microphones | Sensors |
MOSFETs can be used to switch large currents. The voltage at the gate (VGS) of a MOSFET controls the amount of current that flow between the drain and the source (IDS). Almost no current flows into the gate of the MOSFET so a logic gate or op-amp can be connected to the gate and the MOSFET can switch on things that need a large current to work. The MOSFET is turned on when the p.d. between the gate and source is greater than the threshold voltage, VGS(TH)
When choosing a MOSFET you need to consider how much current needs to be switched and
how much power is going to be dissipated in the MOSFET.
The maximum current that can flow through a MOSFET is the saturation current,
(IDSS). The Power in the MOSFET can be calculated from
For information about J-FETs use the link in the table.
| Device | Part number | Picture | Datasheets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small signal n-channel MOSFET | BS170 | Philips Semiconductors | |
| Large signal n-channel MOSFET | IRF520A | 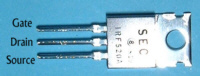 |
International Rectifier |
| Large signal p-channel MOSFET | IRF9520 | 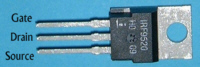 |
International Rectifier |
| Small signal n-channel Junction-FET | BF244 |  |
Fairchild Semiconductor |